History of China: From Ancient Dynasties to Modern Superpower
China is one of the world’s oldest continuous civilizations, with a recorded history stretching back over 5,000 years. Known as the “Middle Kingdom,” it has been a center of culture, philosophy, invention, and political power throughout history. Let’s explore the journey of China from its ancient origins to its rise as a modern global superpower.
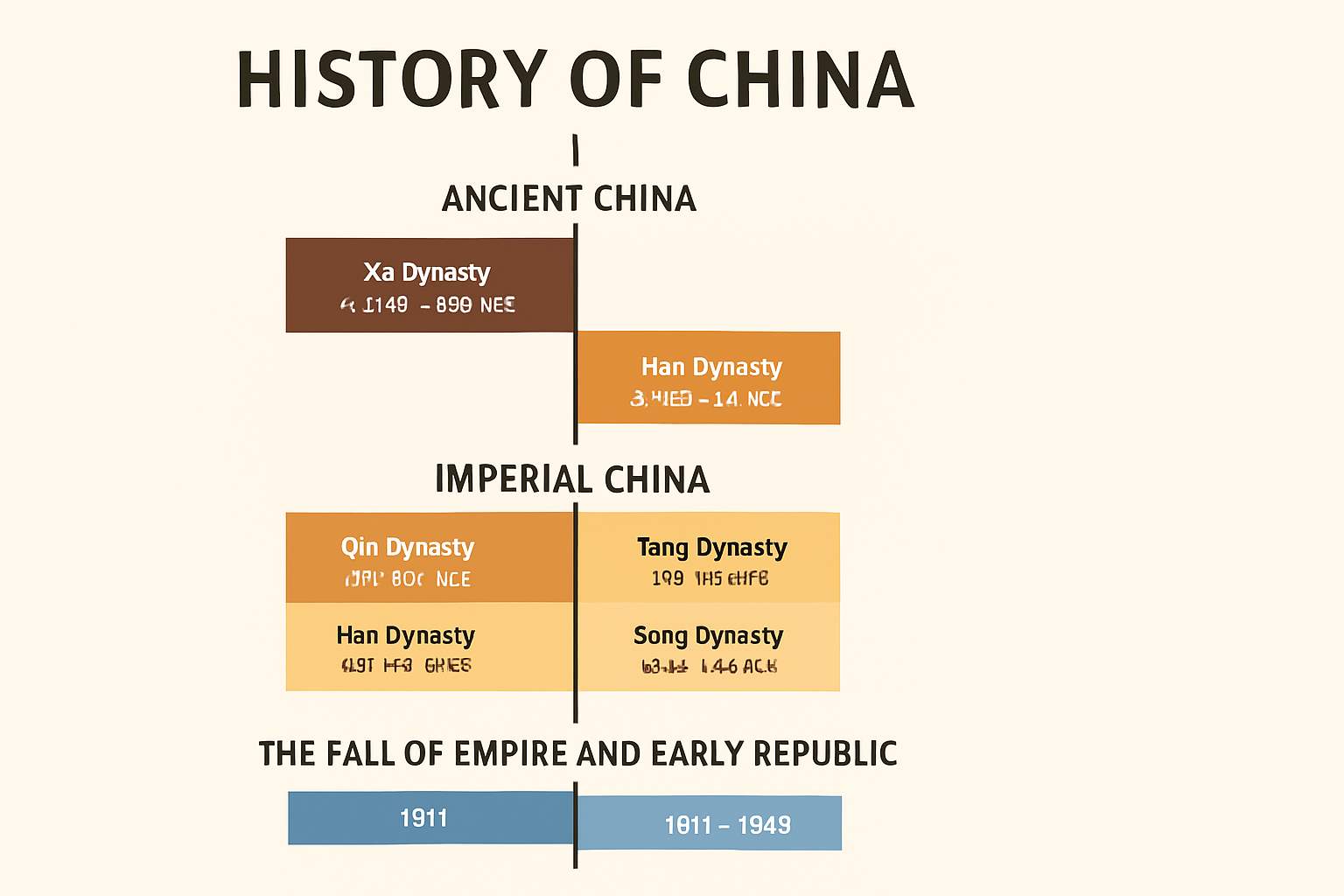
1. Ancient China (c. 2100 BCE – 221 BCE)
- Xia Dynasty (c. 2100 – 1600 BCE): Considered the first Chinese dynasty, though partly legendary.
- Shang Dynasty (c. 1600 – 1046 BCE): Known for bronze work, oracle bones, and early writing.
- Zhou Dynasty (1046 – 221 BCE): Introduced the “Mandate of Heaven,” a political philosophy justifying rulers’ power. Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism emerged during this era.
2. Imperial China (221 BCE – 1911 CE)
- Qin Dynasty (221 – 206 BCE): China’s first empire under Qin Shi Huang, who unified the nation, standardized currency, and began the Great Wall.
- Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE): Expanded trade through the Silk Road, advanced science, medicine, and paper-making. Known as a golden age of Chinese civilization.
- Tang Dynasty (618 – 907 CE): A flourishing era of arts, poetry, and international trade. Buddhism spread widely.
- Song Dynasty (960 – 1279 CE): Innovations in gunpowder, printing, and navigation. The economy and urbanization grew rapidly.
- Yuan Dynasty (1271 – 1368 CE): Established by Mongol leader Kublai Khan. Integrated China into the vast Mongol Empire.
- Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644 CE): Famous for the Forbidden City, Zheng He’s voyages, and strengthening the Great Wall.
- Qing Dynasty (1644 – 1911 CE): The last imperial dynasty, ruled by the Manchus. Expanded China’s territory but faced Western colonial pressures and internal rebellions.
3. The Fall of Empire and Early Republic (1911 – 1949)
- In 1911, the Qing dynasty collapsed, ending 2,000 years of imperial rule.
- Sun Yat-sen founded the Republic of China.
- China faced turmoil: warlordism, Japanese invasion (1937–1945), and a civil war between the Nationalists (Kuomintang) and Communists.
4. People’s Republic of China (1949 – Present)
- 1949: The Communist Party, led by Mao Zedong, established the People’s Republic of China (PRC).
- Mao’s rule brought the Great Leap Forward (1958–1962) and the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976), which caused social and economic disruption.
- After 1978, Deng Xiaoping introduced economic reforms, opening China to global trade and investment.
- Since the 2000s, China has become the world’s second-largest economy, a leader in technology, infrastructure, and global trade.
5. Modern China: A Global Power
Today, China is a rising superpower with influence in geopolitics, technology, and culture. It balances its rich traditions with rapid modernization and global leadership ambitions.
✅ Key Contributions of China to the World:
- Inventions: Paper, printing, gunpowder, compass.
- Philosophies: Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism.
- Architecture: Great Wall, Forbidden City, Terracotta Army.
- Trade: Silk Road and maritime exploration.
Conclusion
The history of China is a remarkable story of resilience, innovation, and transformation. From ancient dynasties to modern skyscrapers, China continues to shape the world with its deep cultural heritage and growing global influence.
FOR YOUR GST BILLING:
ALSO READ THIS “India’s Authentic Hyderabadi Chicken Dum Biryani Recipe
ALSO READ THIS BLOG: Becoming a successful blogging content writer
ALSO READ THIS BLOG: How to Start a Cloud Kitchen: License Setup & Delivery Guide for 2025
please visit my youtube channel : JS TV BY SATHEESH INDIAN https://www.youtube.com/@JSTVNews
చైనా చరిత్ర: ప్రాచీన రాజవంశాల నుండి ఆధునిక సూపర్ పవర్ వరకు
చైనా ప్రపంచంలోనే అత్యంత పాత నిరంతర (సివిలైజేషన్)లలో ఒకటి, దాదాపు 5,000 సంవత్సరాల రికార్డెడ్ చరిత్ర కలిగి ఉంది. “మధ్య రాజ్యం” (Middle Kingdom)గా ప్రసిద్ధి చెందిన చైనా, చరిత్ర అంతటా సంస్కృతి, తత్వశాస్త్రం, ఆవిష్కరణలు మరియు రాజకీయ శక్తికి కేంద్రంగా నిలిచింది. ఇప్పుడు మనం చైనాను తన ప్రాచీన ఆవిర్భావం నుండి ఆధునిక గ్లోబల్ సూపర్ పవర్గా ఎదిగిన ప్రయాణాన్ని తెలుసుకుందాం.
1. ప్రాచీన చైనా (సుమారు క్రీ.పూ. 2100 – 221)
- శియా వంశం (సుమారు క్రీ.పూ. 2100 – 1600): చైనా తొలి రాజవంశంగా భావిస్తారు, అయితే ఇది కొంతమేరకు పౌరాణికం.
- శాంగ్ వంశం (సుమారు క్రీ.పూ. 1600 – 1046): కంచు పనులు, ఆరాకల్ ఎముకలు, ప్రాథమిక రచనా శైలి కోసం ప్రసిద్ధి.
- జౌ వంశం (క్రీ.పూ. 1046 – 221): “మండేట్ ఆఫ్ హెవెన్” అనే రాజరిక తత్వాన్ని పరిచయం చేసింది. కన్ఫ్యూషియనిజం, తావిజం, లీగలిజం ఈ కాలంలో ఉద్భవించాయి.
2. సామ్రాజ్య చైనా (క్రీ.పూ. 221 – క్రీస్తు 1911)
- చిన్ వంశం (క్రీ.పూ. 221 – 206): చైనా మొదటి సామ్రాజ్యంగా చిన్ షి హువాంగ్ పాలనలో ఏర్పడింది. దేశం ఏకీకృతం, కరెన్సీ ప్రమాణీకరణ, గ్రేట్ వాల్ నిర్మాణం ప్రారంభం.
- హాన్ వంశం (క్రీ.పూ. 206 – క్రీస్తు 220): సిల్క్ రోడ్ ద్వారా వాణిజ్య విస్తరణ, శాస్త్రం, ఔషధం, కాగితం తయారీ పురోగతి. చైనా చరిత్రలో స్వర్ణ యుగంగా భావిస్తారు.
- తాంగ్ వంశం (618 – 907): కళలు, కవిత్వం, అంతర్జాతీయ వాణిజ్యం అభివృద్ధి చెందిన యుగం. బౌద్ధం విస్తరించింది.
- సాంగ్ వంశం (960 – 1279): గన్పౌడర్, ముద్రణ, నావికతలో ఆవిష్కరణలు. ఆర్థిక మరియు పట్టణీకరణ వేగంగా అభివృద్ధి.
- యువాన్ వంశం (1271 – 1368): మొంగోలు నేత కుబ్లాయ్ ఖాన్ చైనాను పాలించిన రాజవంశం. మొంగోలియా సామ్రాజ్యంలో చైనాను కలిపారు.
- మింగ్ వంశం (1368 – 1644): ఫోర్బిడెన్ సిటీ, జెంగ్ హే యాత్రలు, గ్రేట్ వాల్ పునర్నిర్మాణం ప్రసిద్ధి.
- చింగ్ వంశం (1644 – 1911): చివరి సామ్రాజ్య వంశం, మాంచూ ప్రజల పాలన. విదేశీ కాలనీల ఒత్తిడి, అంతర్గత తిరుగుబాట్లు ఎదురయ్యాయి.
3. సామ్రాజ్య పతనం మరియు ప్రారంభ గణతంత్రం (1911 – 1949)
- 1911లో చింగ్ వంశం పతనమై, 2000 సంవత్సరాల సామ్రాజ్య పాలన ముగిసింది.
- సన్ యట్-సెన్ చైనా గణతంత్రాన్ని స్థాపించాడు.
- తరువాత దేశం రాజకీయ అశాంతితో ఎదురైంది: వార్లార్డ్ పాలన, జపాన్ ఆక్రమణ (1937–1945), మరియు క్వామింటాంగ్ (జాతీయవాదులు) మరియు కమ్యూనిస్టుల మధ్య పౌర యుద్ధం.
4. చైనా ప్రజాస్వామ్య ప్రజా గణతంత్రం (1949 – ప్రస్తుతం)
- 1949లో మావో జెడాంగ్ నేతృత్వంలో కమ్యూనిస్ట్ పార్టీ ప్రజా గణతంత్ర చైనాను స్థాపించింది.
- మావో పాలనలో: గ్రేట్ లీప్ ఫార్వర్డ్ (1958–1962), కల్చరల్ రివల్యూషన్ (1966–1976) జరగ్గా, భారీ సామాజిక, ఆర్థిక దెబ్బలు తగిలాయి.
- 1978 తర్వాత, డెంగ్ షియాపింగ్ ఆర్థిక సంస్కరణలు ప్రవేశపెట్టి, చైనాను గ్లోబల్ ట్రేడ్, పెట్టుబడులకు తెరిచాడు.
- 2000ల నుండి, చైనా ప్రపంచంలో రెండవ అతిపెద్ద ఆర్థిక వ్యవస్థగా, సాంకేతికత, మౌలిక సదుపాయాలు మరియు అంతర్జాతీయ వాణిజ్యంలో ముందంజలో ఉంది.
5. ఆధునిక చైనా: గ్లోబల్ శక్తిగా ఎదుగుతుంది
ఈరోజు చైనా ప్రపంచ రాజకీయాలు, సాంకేతికత మరియు సంస్కృతిలో కీలక పాత్ర పోషిస్తుంది. దీని సంపన్న సంప్రదాయాలను నిలుపుకుంటూనే వేగంగా ఆధునికతను స్వీకరిస్తూ, ప్రపంచ నాయకత్వ లక్ష్యాలను ముందుకు తీసుకెళ్తోంది.
✅ ప్రపంచానికి చైనా చేసిన ముఖ్యమైన కృషులు:
- ఆవిష్కరణలు: కాగితం, ముద్రణ, గన్పౌడర్, కాంపస్.
- తత్వశాస్త్రాలు: కన్ఫ్యూషియనిజం, తావిజం, లీగలిజం.
- వాస్తుశిల్పం: గ్రేట్ వాల్, ఫోర్బిడెన్ సిటీ, టెర్రకోట ఆర్మీ.
- వాణిజ్యం: సిల్క్ రోడ్, సముద్ర యాత్రలు.
ముగింపు
చైనా చరిత్ర అనేది ఓ అసాధారణ గాధ — ఇది ప్రతిఘటన, ఆవిష్కరణ, పరివర్తనలతో నిండి ఉంది. ప్రాచీన రాజవంశాల నుండి ఆధునిక స్కైస్క్రేపర్ల వరకు, చైనా తన గొప్ప సంస్కృతి వారసత్వంతో పాటు ప్రపంచంపై పెరుగుతున్న ప్రభావాన్ని కొనసాగిస్తోంది.